Molecular model of penicillin by Dorothy M Crowfoot Hodgkin, England, 1945
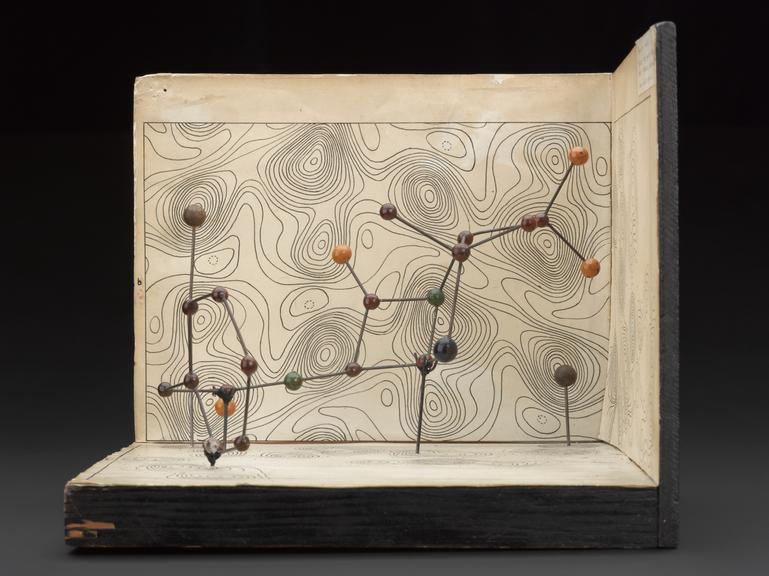
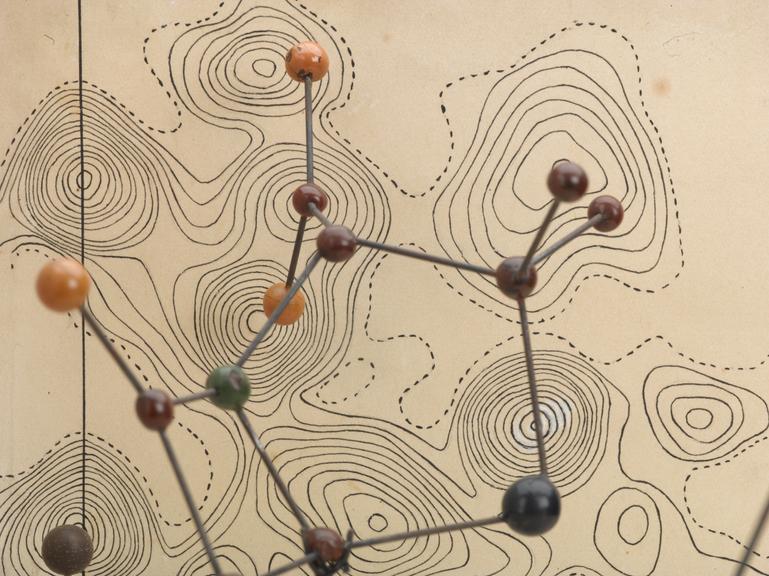
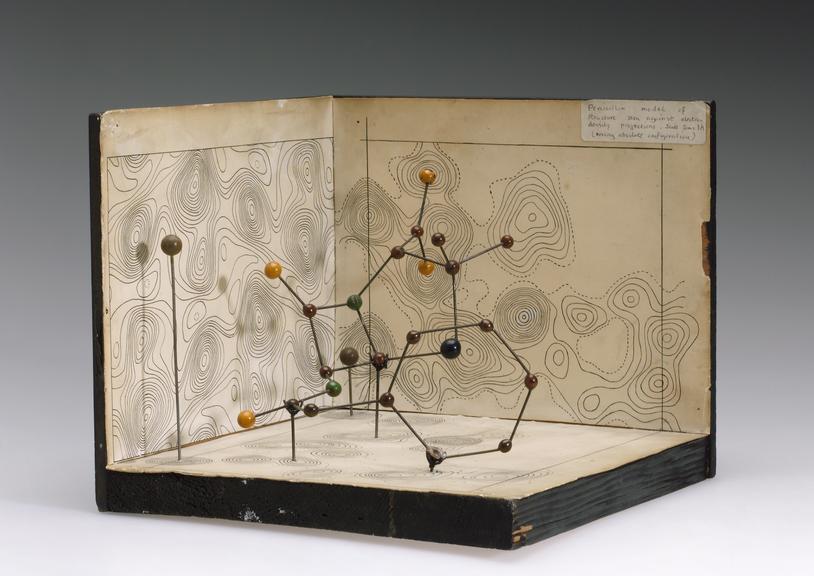





















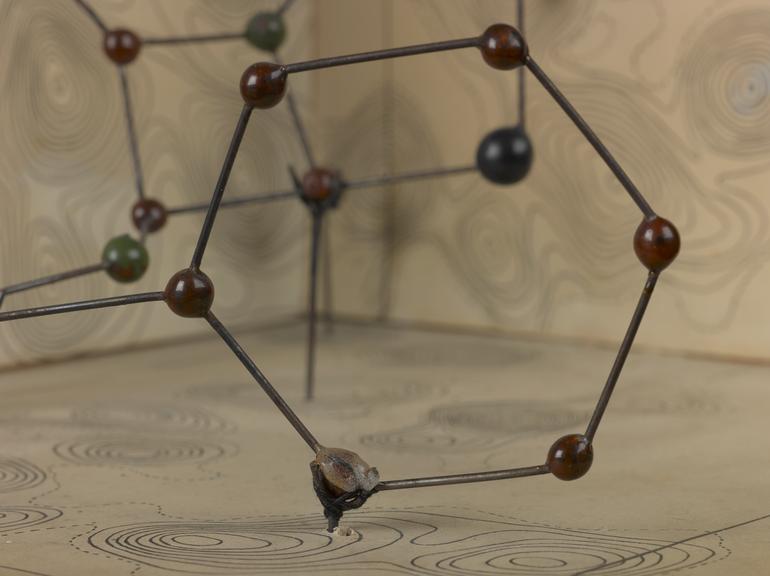




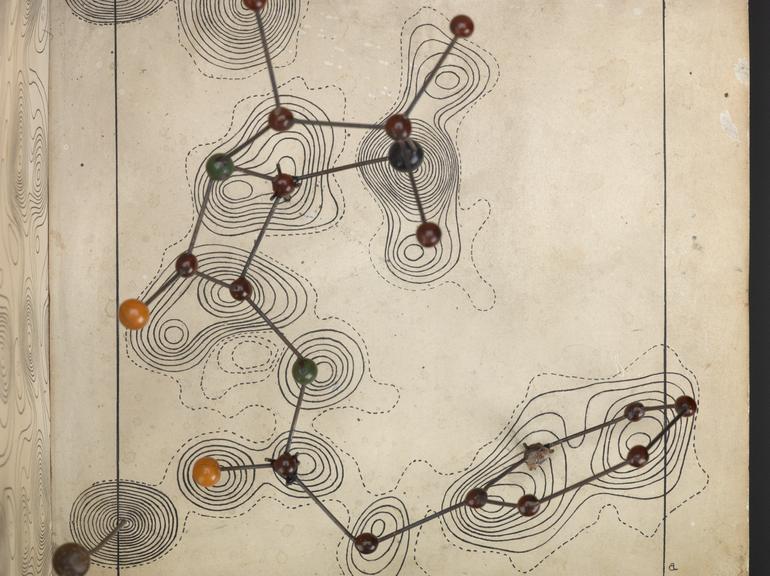
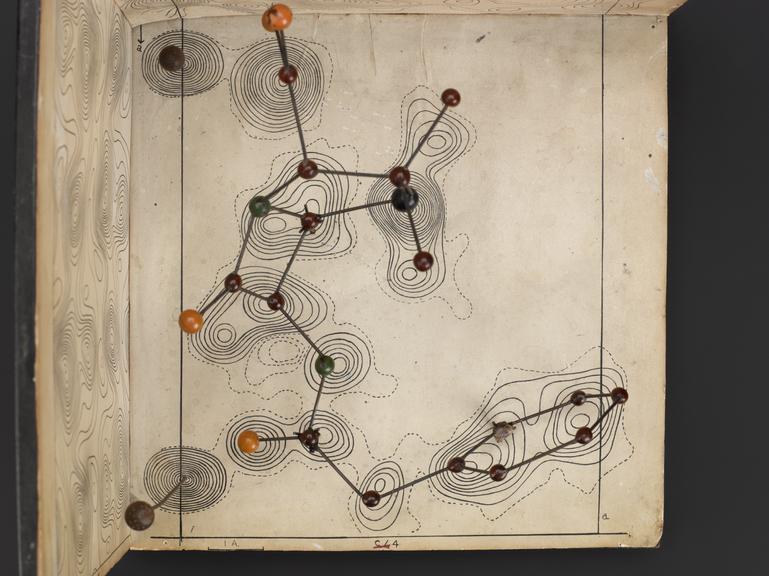

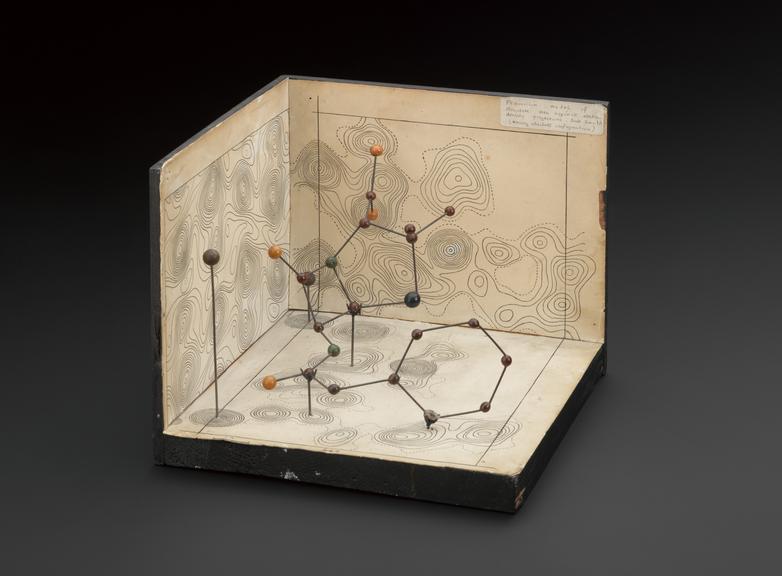




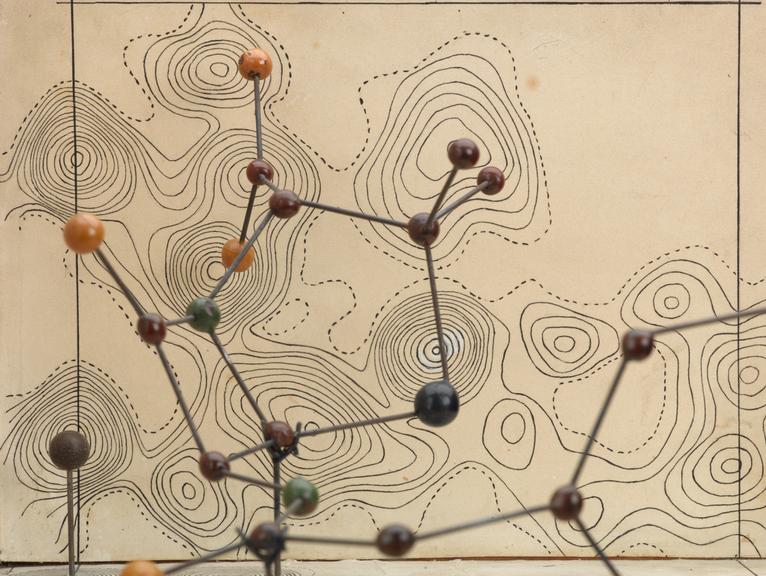





Penicillin; molecular model by Dorothy Hodgkin, ca. 1945.
Penicillin was successful as an antibiotic and treatment for infection well before scientists knew its chemical nature. Chemist and crystallographer Dorothy M Crowfoot Hodgkin (1910-1994) used large punch-card operated tabulators, predecessor to the computer, to help analyse the patterns cast by reflected X-rays. This technique is known as X-ray crystallography.
Hodgkin later won the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1964 “for her determinations by X-ray techniques of the structures of important biochemical substances”.
Details
- Category:
- Biochemistry
- Object Number:
- 1996-686
- Materials:
- pine (wood), paper (fibre product), plastic (unidentified), paint, steel (metal) and wood (unidentified)
- Measurements:
-
overall: 170 mm x 200 mm x 200 mm, .64 kg
- type:
- penicillin
- credit:
- Luke Hodgkin