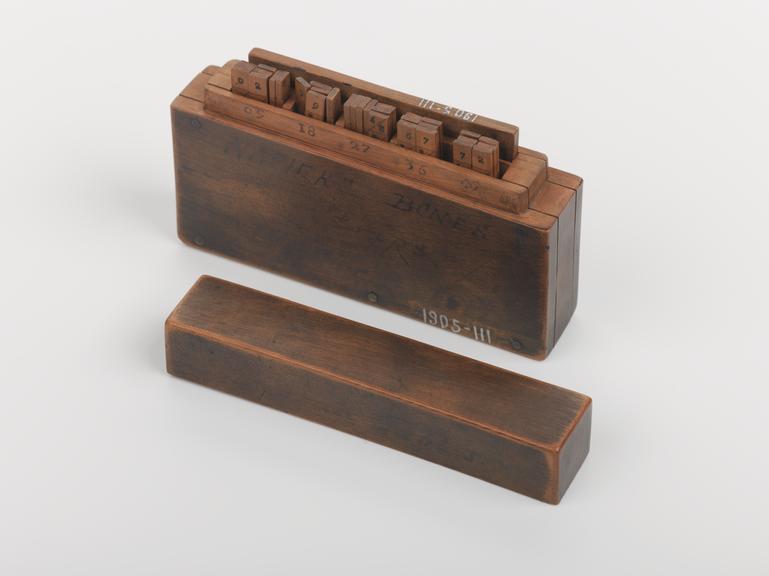
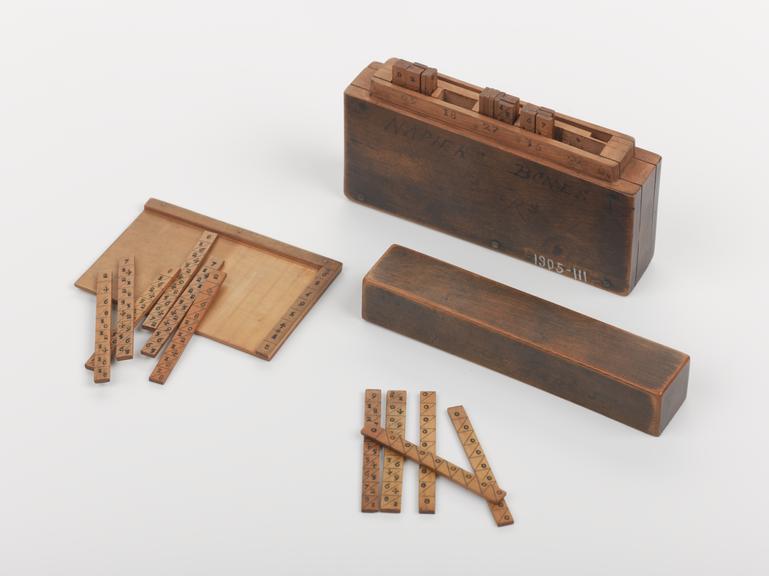
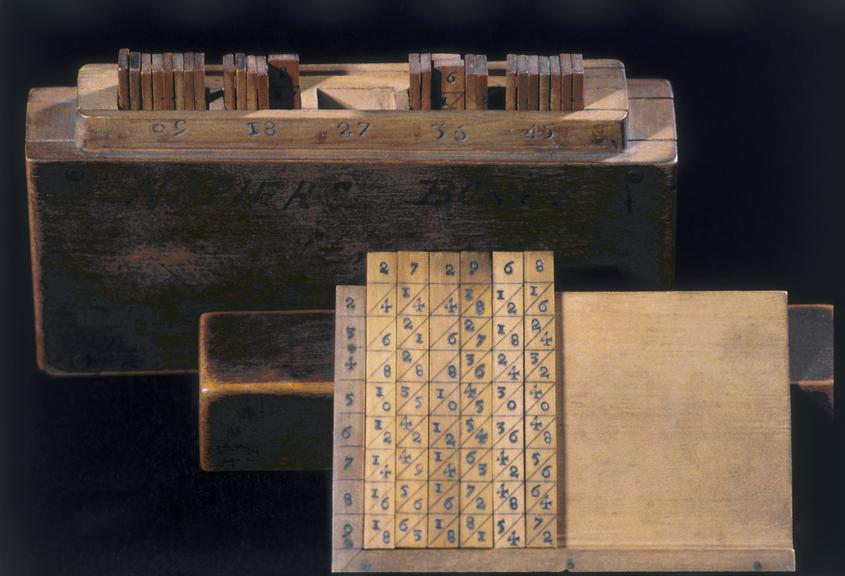
Set of Napier's rods in boxwood case, made in England by an unknown maker, about 1690.
John Napier (1550-1617), discoverer of logarithms, designed this popular calculating tool known as Napier's cylindrical 'rods' or 'bones'. The 'bones' consist of a set of rectangular rods, each marked with a counting number at the top, and the multiples of that number down their lengths. When aligned against the row of multiples as shown, any multiple of the top number can be read off from right to left by adding the digits in each parallelogram in the appropriate row. Multiplication is thus reduced to addition and the bones can also be used for division and to calculate square roots.
Details
- Category:
- Mathematics
- Object Number:
- 1905-111
- Materials:
- box (wood)
- Measurements:
-
Overall: 57 mm x 95 mm x 20 mm, 0.08 kg
- type:
- napier's bones
- credit:
- Major-General H.P. Babbage