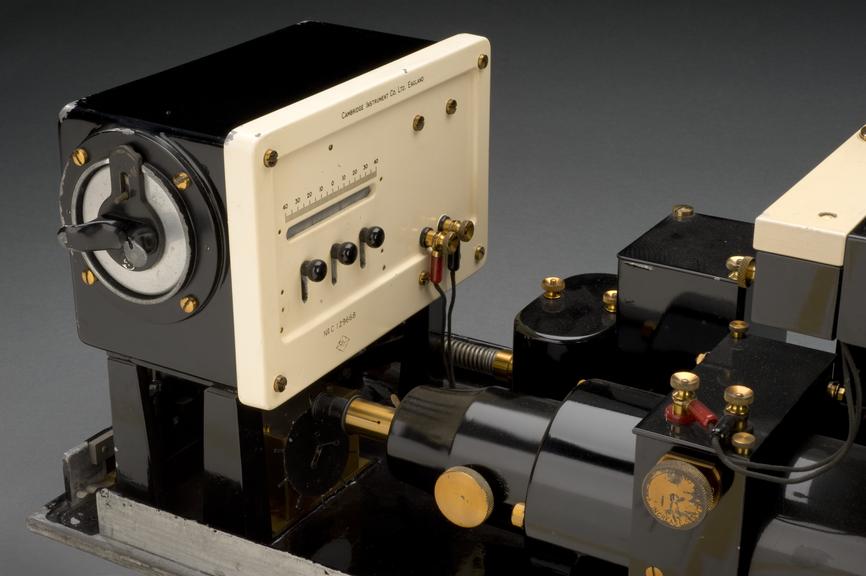
Portable electrocardiograph, Cambridge, England, 1929
Portable electrocardiograph machine, No.C129668, by the Cambridge Instrument Co. Ltd., 1929.
More
An electrocardiograph produces ‘traces’ or visual graphical records of the electrical activity in a person’s heart. The records are called electrocardiograms or ECGs. Physicians examine them for irregularities that indicate disease, birth defects or heart attacks. This example was made by the Cambridge Scientific Instrument Co Ltd.
The first human electrocardiogram was made by Englishman A. D. Waller (1856-1922) in 1887. However, the modern practice of electrocardiography was made possible by a device called the ‘string galvanometer’. This was invented around 1903 by Dutch physiologist Willem Einthoven (1860-1927). Einthoven won the Nobel Prize for Physiology/Medicine for his invention. Cambridge Scientific Instrument Company made the first commercial machine in 1908.
- Measurements:
-
overall: 340 mm x 580 mm x 290 mm,
- Materials:
- aluminium (metal) , copper (alloy) , iron , plastic (unidentified) , painted coating , lacquer and fibre (unidentified)
- Object Number:
- 1979-204 Pt1
- type:
- electrocardiograph
- Image ©
- The Board of Trustees of the Science Museum