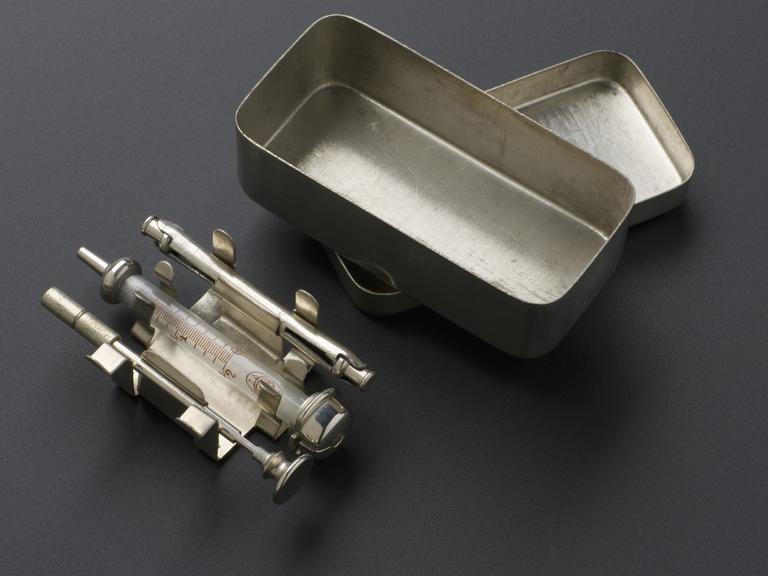
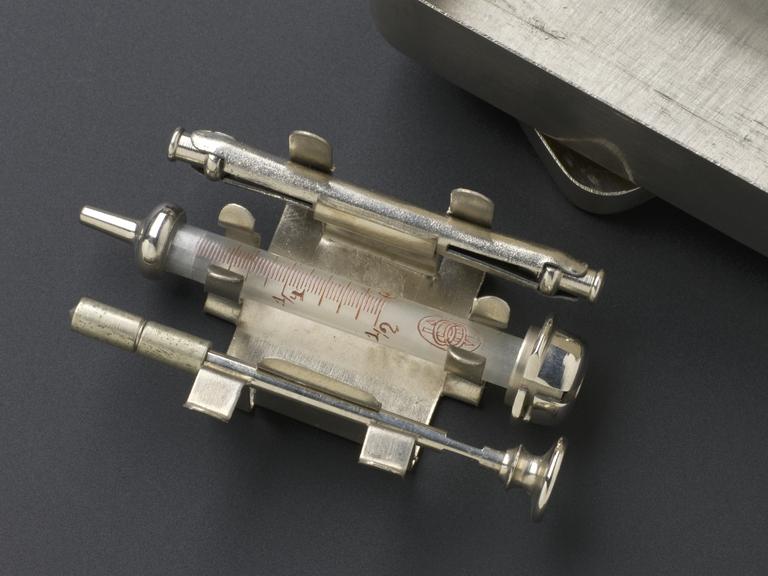
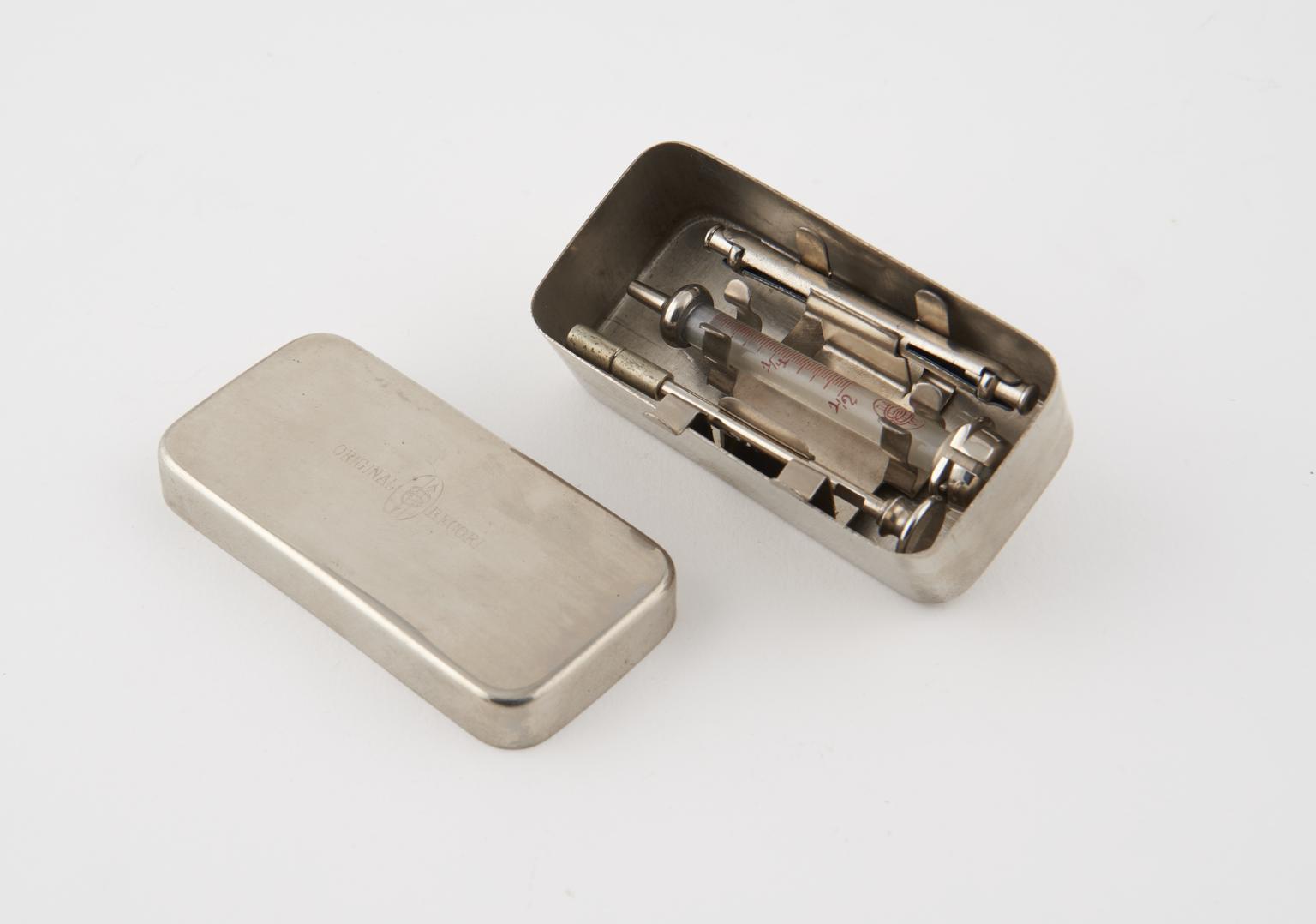
Tuberculin hypodermic syringe, Germany, 1901-1930
Hypodermic syringe, steel and glass, for tuberculin, in metal case with lid and brass wire pieces, possibly German, 1901-1930 (see note).
More
Tuberculin is injected into the skin to see whether a person has been exposed to tuberculosis-causing bacteria. If the skin shows a reaction after 48 hours, they have been exposed. The tests help catch the disease before it develops and prevents its spread. This type of test is known as the Mantoux test, named after Charles Mantoux (1877-1947), who invented it in 1907. The test is still used today, especially to confirm the results of other tuberculosis tests.
- Materials:
- steel (metal) , glass , steel plated , metal (unknown) and brass (copper, zinc alloy)
- Object Number:
- 1981-987/1
- type:
- hypodermic syringe
- Image ©
- The Board of Trustees of the Science Museum