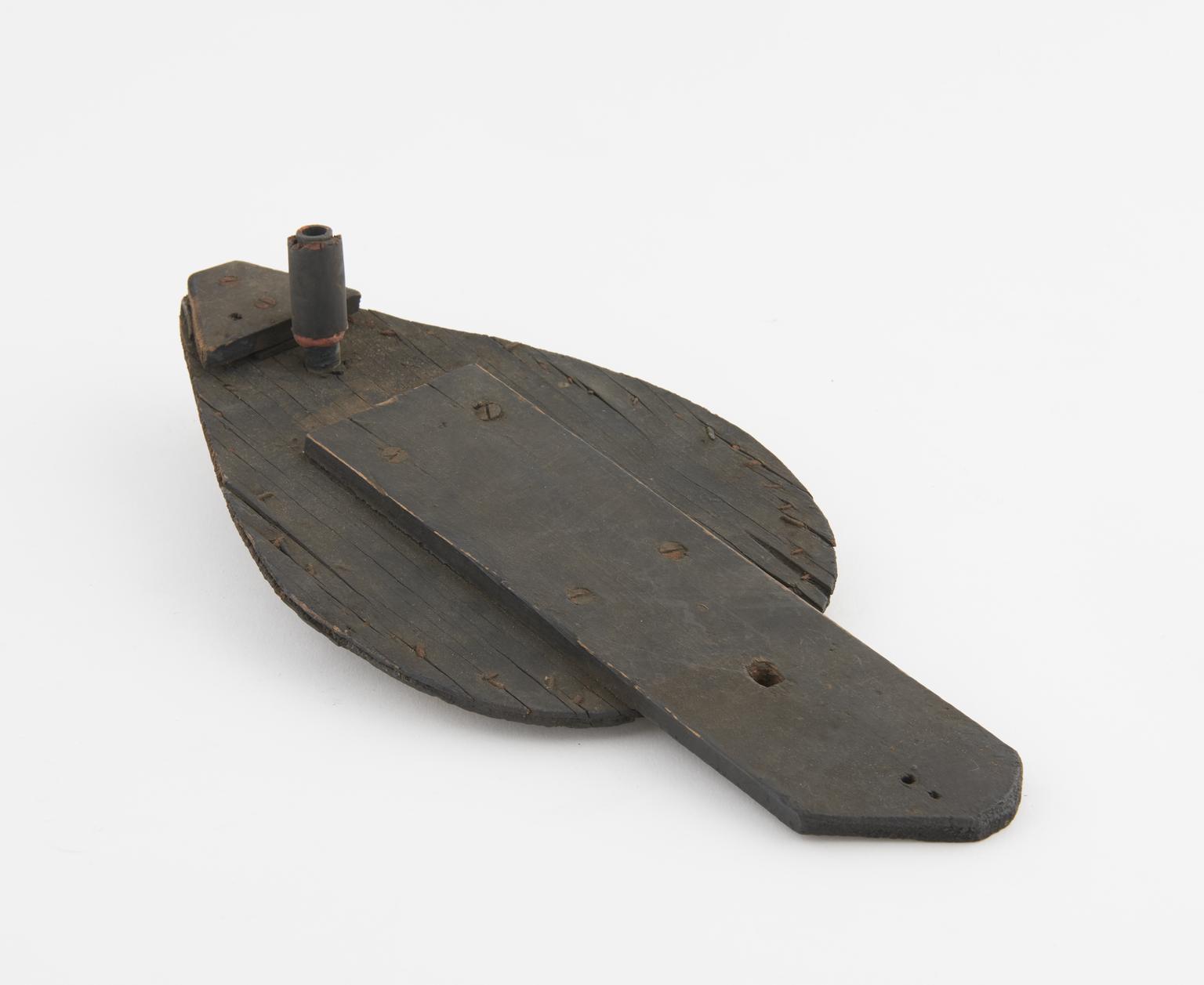
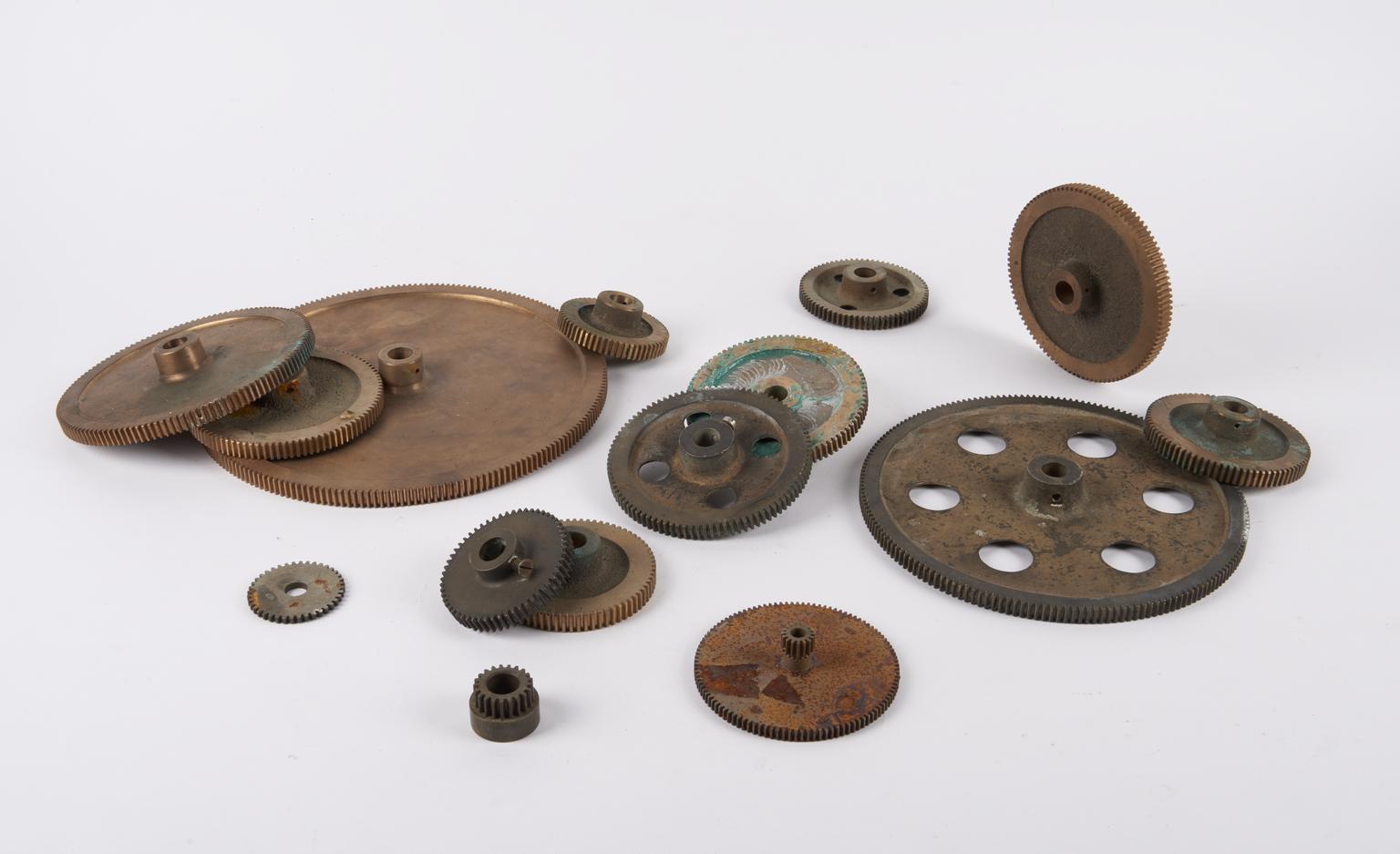
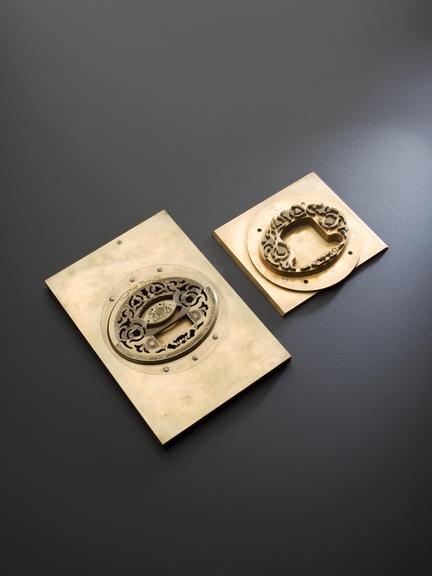
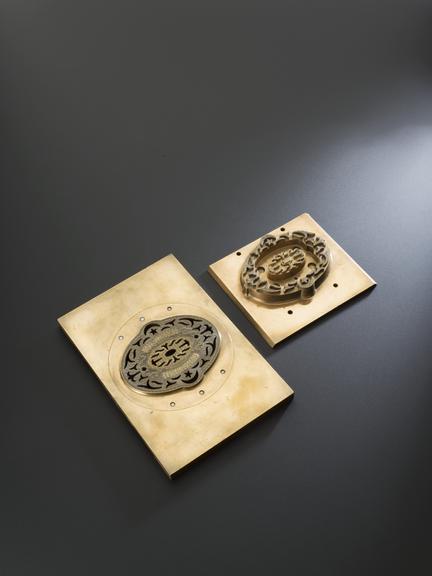
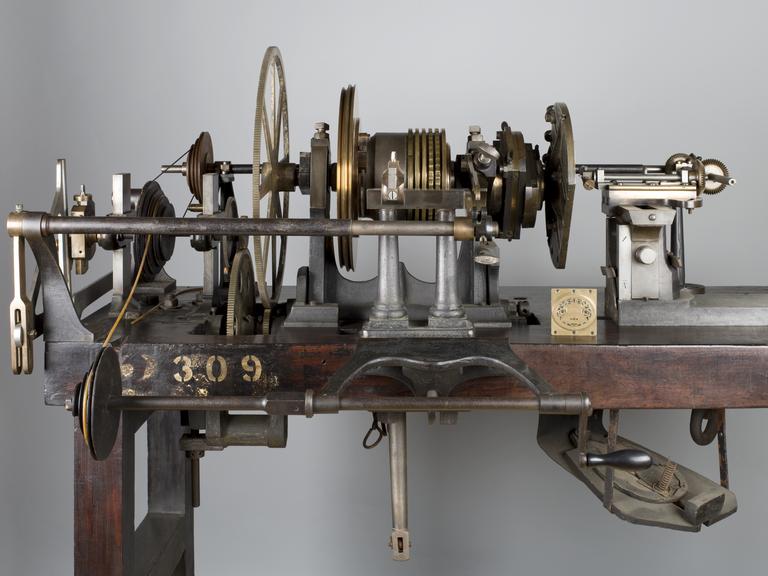
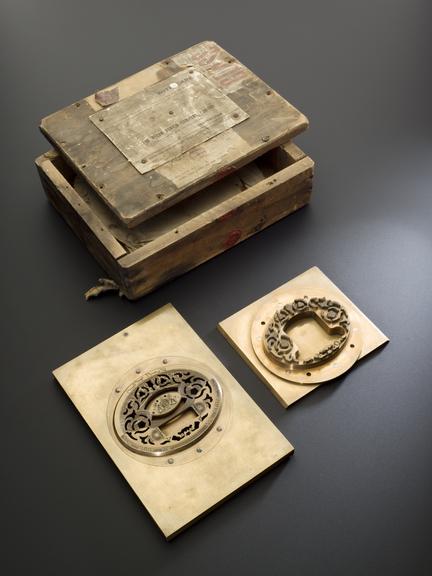
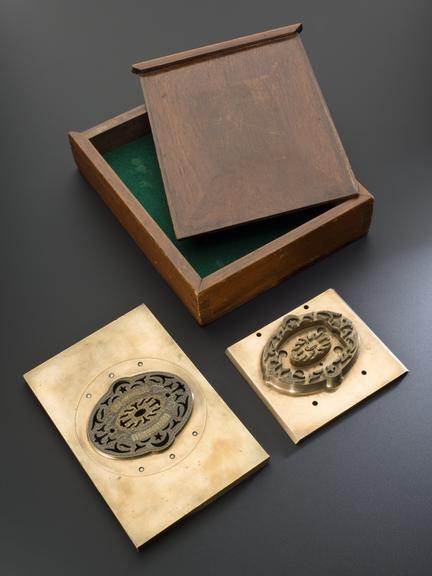
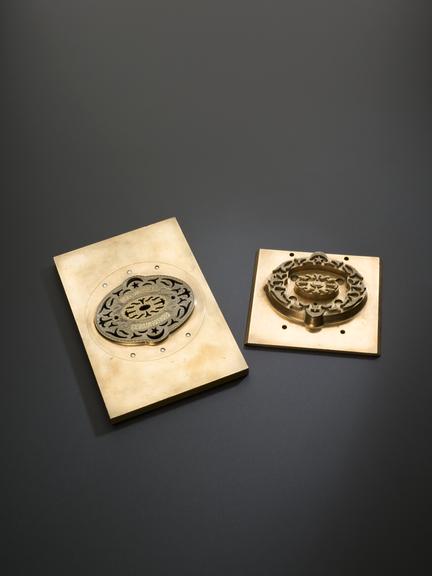
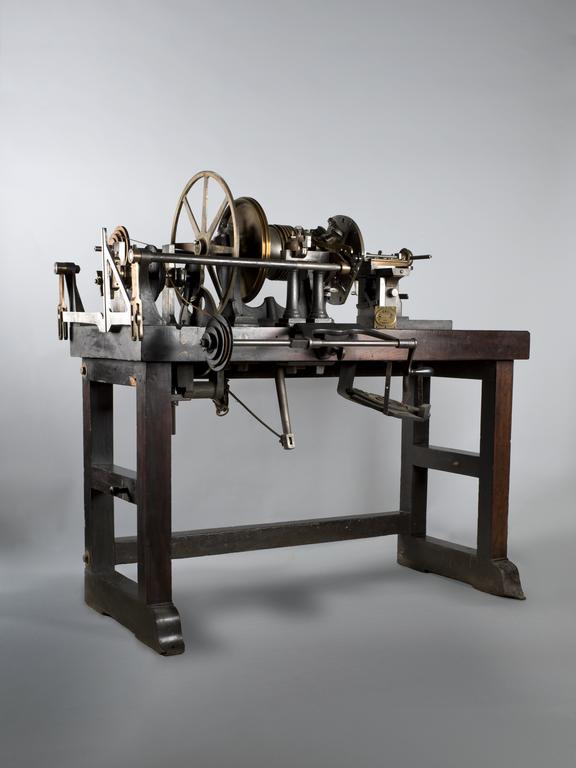
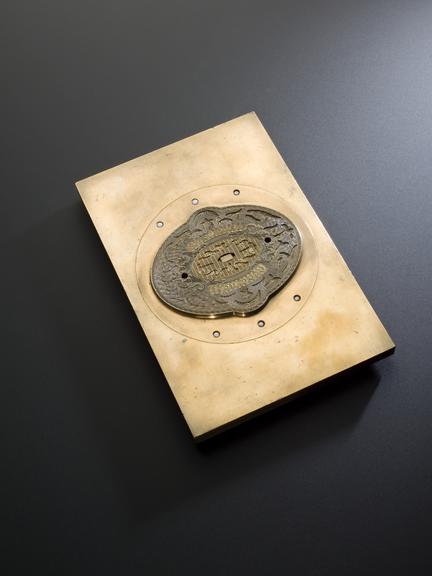
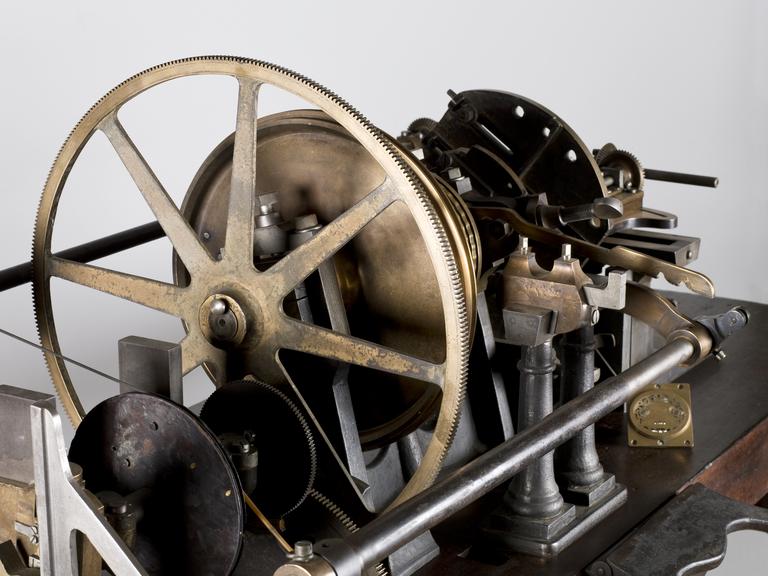
Rose engine lathe used to manufacture compound printing plates, built by Bryan Donkin, London, 1821.
- Materials:
- mahogany (wood) , wrought iron , cast iron , gunmetal and paint
- Object Number:
- 2008-26/1
- type:
- rose engine













Rose engine lathe used to manufacture compound printing plates, built by Bryan Donkin, Bermondsey, London, 1820.
Sir William Congreve patented a process known as compound-plate printing in 1821, and the printing plates were engraved using this machine. It was devised primarily as a means of preventing forgery – from 1797 until 1821 Britain depended solely on paper currency, and in the decade to 1820 detected counterfeiting cases rose by more than 500%. Compound printing became widely used for producing duty stamps, postage stamps and much else from the 1820s onwards - but not for manufacturing banknotes, where a combination of techniques which also included compound printing, were applied.
Congreve’s concept was completely new, and he gave the practical project of making it work to Bryan Donkin. The process consists of highly detailed two-colour printing. This was done using a printing plate comprising two intricate and interlocking parts, an upper part fitting through appropriately-shaped apertures in the lower part. The two parts were separated vertically so that two different colour inks could be applied (one to each) and then they were brought together and the impression made on paper. Most importantly, the detail engraved on the two-part plate was made while they were fitted together, so any potential forgers were faced with the near-impossible challenge of not only reproducing the complex mathematical shapes generated by the machine, but also duplicating the colour changes for each individual line exactly.