Solar cells in lucite
- Made:
- 1990-1995
- maker:
- European Space Agency
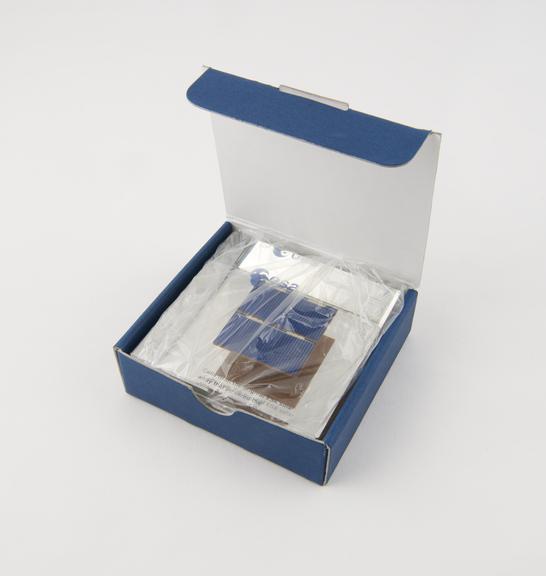

Solar cells in lucite, from the original ESA solar array that powered the Hubble Space Telescope, used in orbit from April 1990 to December 1993, in blue cardboard box, by European Space Agency, 1990-1995
The Hubble Space Telescope was launched in 1990 with multi-national co-operation. Named after astronomer Edwin Hubble, it has become an iconic part of space history, with NASA claiming it has changed our fundamental understanding of the universe. It has also provided detailed and beautiful imagery of the universe that has influenced design and fashion trends.
The Telescope relies on solar power, provided by cells distributed on wing-like arrays to absorb as much light as possible. These solar cells have a limited lifespan, and Hubble’s first set were replaced in 1993.
This is an example of some of the original solar cells that powered Hubble between 1990 and 1993. Scientists studied the effects of the mission on the cells when they returned to Earth and concluded that they were ‘hit daily by as many as 1000 small (0.001 mm or 1 micron-sized) objects’.