Atomic Oscillator Clock
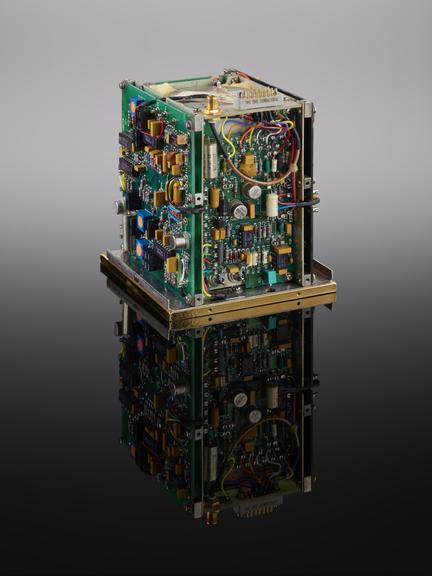
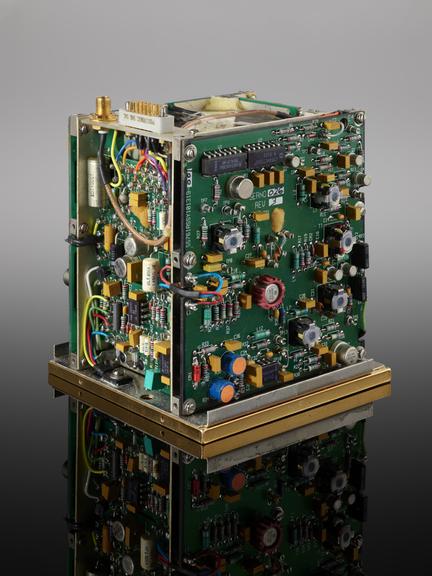
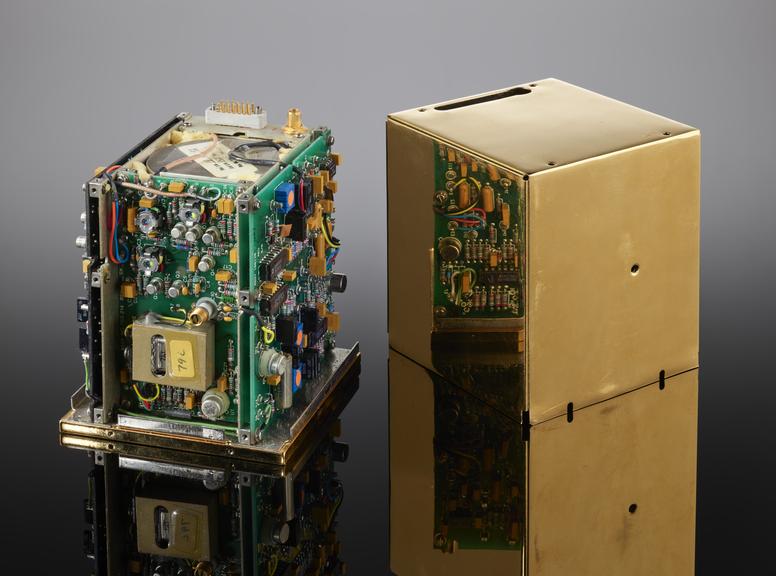
Atomic Oscillator Clock, Model FRK, by Efratom GmbH, Munich, as used to baseline the key concepts and hardware for the Global Positioning System (GPS) 1971-1974, and presented complete with gold cover to Hugo Fruehauf, the Chief Engineer for the GPS system, upon his departure from Efratom in 1996.
More
The success of the Global Positioning System (usually known by its acronym, GPS) depends on each of the constellation of satellites being able to calculate its exact position. To do this, each relies on very high precision timepieces. The first iteration of the GPS system used timepieces which were developed from the Efratom Model FRK, and this particular item was given to the GPS system's chief engineer upon his retiring from Efratom in 1996.
- Materials:
- gold (metal) , copper (metal) , steel (metal) and plastic (unidentified)
- Object Number:
- 2022-1409/1
- type:
- atomic clock