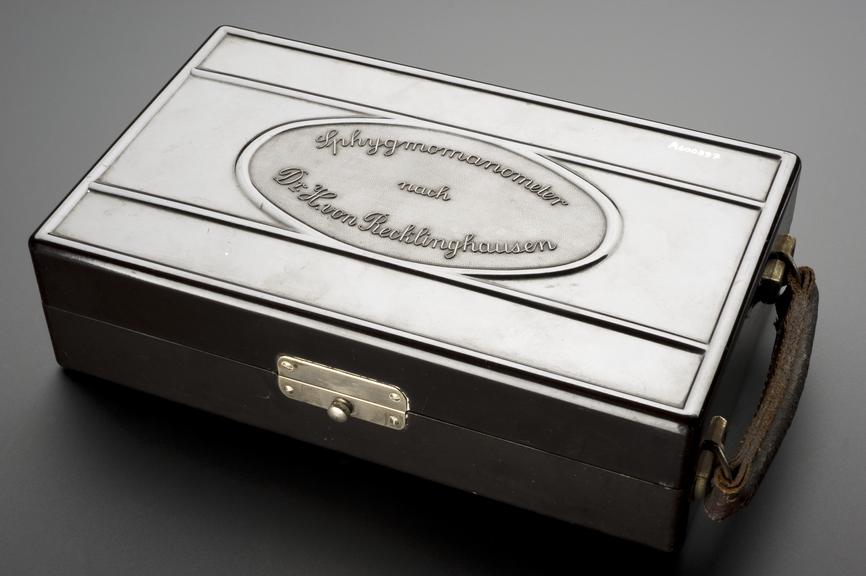




Recklinghausen tonometer (sphygmomanometer), in case
This tonometer is a type of sphygmomanometer. A sphygmomanometer measured the force, rate and variations in the pulse. The tonometer consists of two overlapping cuffs. It measures the systolic and diastolic blood pressure. This means the force that blood flows with from the heart into the arteries and the forces as the heart relaxes and fills again with blood. It is the commonest technique for measuring blood pressure. It is also completely safe.
This device was developed by Heinrich von Recklinghausen (1867-1942) in the 1920s. He was a leading researcher in blood pressure and blood pressure measurement.
Details
- Category:
- Clinical Diagnosis
- Collection:
- Sir Henry Wellcome's Museum Collection
- Object Number:
- A600397
- Materials:
- plastic, rubber, metal (unknown), glass and complete
- Measurements:
-
overall (case closed): 70 mm x 270 mm x 155 mm, 1.336 kg
overall (case open): 193 mm x 270 mm x 190 mm, 1.336 kg
- type:
- sphygmomanometer
- credit:
- Charing Cross Hospital Medical School. D




