Thoma haemacytometer counting chamber
1891-1930
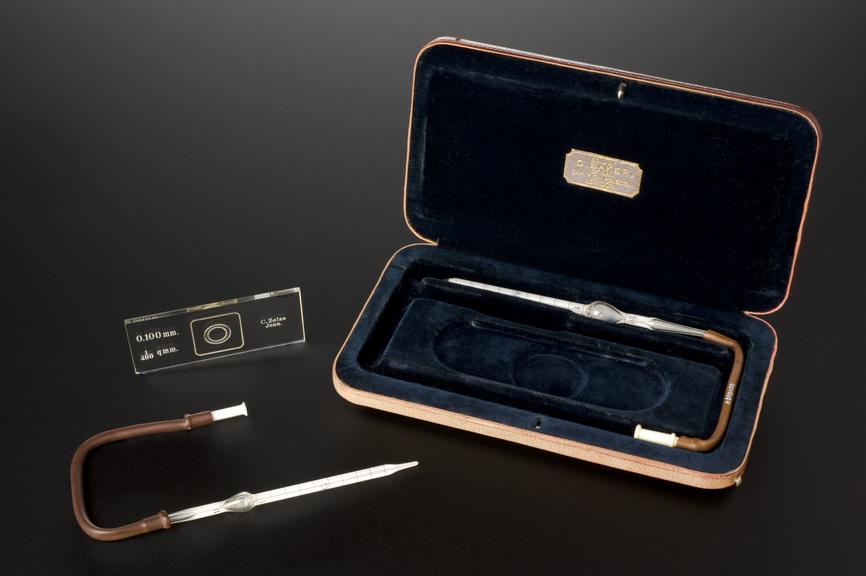
Thoma haemacytometer with pipettes, counting chamber in leatherette case, by C. Zeiss, German, 1891-1930
A haemacytometer calculates the number of blood cells within a given amount of blood. The first haemacytometer was invented by German physician, Karl Vierordt (1818-84) in 1852. His invention was later adapted by many others. Any increase or decrease in blood cells in the blood is analysed. It may indicate disease within the body. A low level of red blood cells is called anaemia. A high level of red blood cells is called polycythaemia. This haemacytometer is seen with pipettes and counting chamber. It was made by Carl Zeiss in Jena, Germany.